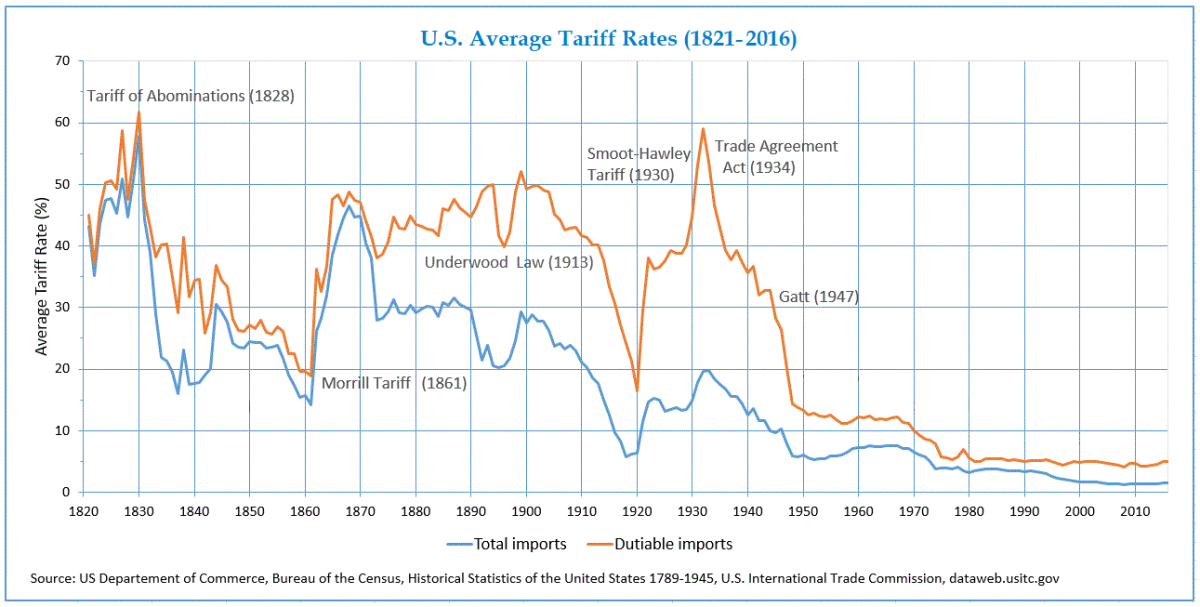
A tariff is basically a tax that a government puts on goods coming from other countries. These taxes are usually put in place to make things that come from other countries more expensive, which can make people want to buy products made within their own country instead.
For example, if a country has a high tariff on imported cars, it makes foreign cars more expensive. This might encourage people to buy cars made in their own country, which helps local businesses and keeps jobs in the country. On the other hand, it can also mean higher prices for consumers, which isn’t always great for people trying to save money.
Tariffs are often used as a tool to protect local industries from competition. Countries might also use tariffs to push other countries to make trade deals or follow certain rules. However, tariffs can also lead to problems, like trade wars, where countries keep raising tariffs on each other, making things even more expensive for everyone.
In short, tariffs are a way for governments to control trade, protect businesses, and raise money, but they also come with some downsides like higher prices and potential conflicts with other countries.